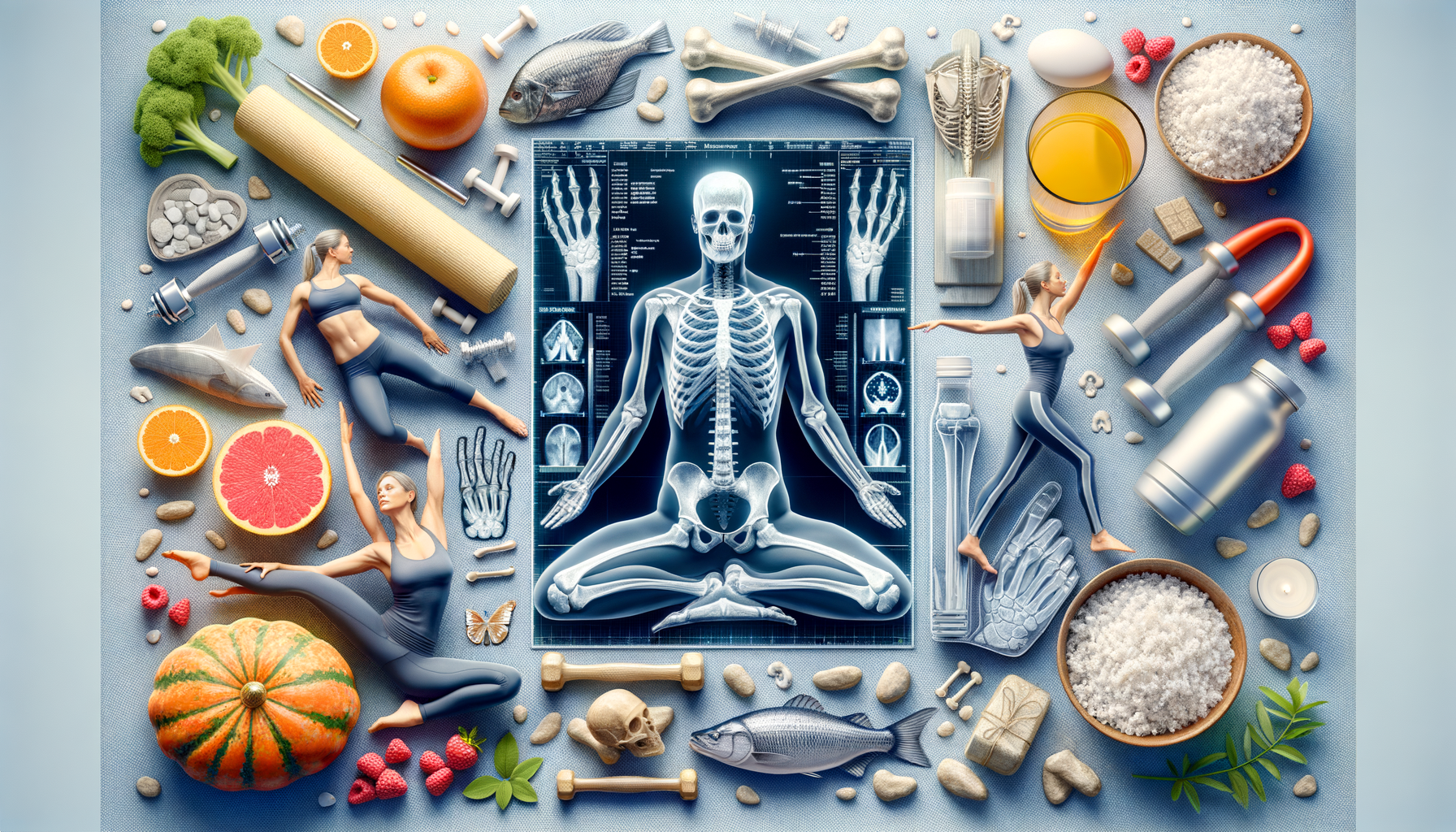
Understanding Osteoporosis: Causes and Impact
Osteoporosis, often referred to as the “silent disease,” is a condition characterized by weakened bones, increasing the risk of sudden and unexpected fractures. This condition primarily affects older adults, particularly postmenopausal women. The bones lose density and become more fragile, which is why understanding the causes and impact of osteoporosis is crucial for prevention and management.
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including hormonal changes, particularly decreased estrogen levels in women and testosterone in men. Additionally, inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking are significant risk factors. Genetics also play a role, as those with a family history of osteoporosis are more likely to develop the condition.
The impact of osteoporosis extends beyond physical health, affecting emotional and social well-being. Fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, or wrist, can lead to chronic pain and disability, significantly affecting the quality of life. Understanding these factors emphasizes the importance of early detection and proactive management to mitigate the risks associated with osteoporosis.
Identifying Osteoporosis Symptoms
Osteoporosis is often asymptomatic until a fracture occurs, making early identification challenging. However, there are subtle signs that may indicate the onset of the disease. One of the most common symptoms is a noticeable loss of height over time, often accompanied by a stooped posture. This occurs due to vertebral fractures or collapse, which can happen silently without any noticeable pain.
Back pain, particularly in the lower back, can also be an early symptom of osteoporosis. This pain is often due to compression fractures in the spine. Moreover, brittle nails and a decrease in grip strength can be subtle indicators of reduced bone density. While these symptoms are not definitive, they warrant further investigation, particularly in individuals with risk factors for osteoporosis.
Regular bone density tests, such as a DEXA scan, are crucial for early detection. These tests measure bone mineral density and help in assessing the risk of fractures. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, reducing the risk of severe complications associated with osteoporosis.
Effective Treatments for Osteoporosis
Treating osteoporosis involves a multifaceted approach aimed at strengthening bones and preventing fractures. Medications are often prescribed to help slow bone loss and increase bone density. These include bisphosphonates, which are commonly used to prevent the loss of bone mass, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) that mimic estrogen’s beneficial effects on bone density.
In addition to medications, adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone health. These nutrients are vital for maintaining bone density and strength. Calcium can be obtained from dietary sources such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, while vitamin D can be synthesized through sunlight exposure and is also available in supplements.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be considered for postmenopausal women to maintain bone density, although it is not suitable for everyone and requires careful evaluation of risks and benefits. Lifestyle modifications, including quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and engaging in regular physical activity, are also crucial components of osteoporosis treatment.
Exercise for Osteoporosis: Building Stronger Bones
Exercise plays a pivotal role in managing osteoporosis and improving bone health. Weight-bearing and resistance exercises are particularly effective in maintaining and building bone density. Weight-bearing exercises include activities such as walking, jogging, and dancing, which force the body to work against gravity, thereby strengthening bones.
Resistance exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, help build muscle strength, which in turn supports and protects the bones. These exercises not only enhance bone density but also improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and subsequent fractures.
Incorporating flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, can further enhance bone health by improving posture and reducing the likelihood of falls. It is important for individuals with osteoporosis to consult with healthcare professionals or physical therapists to develop a safe and effective exercise regimen tailored to their specific needs and capabilities.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a significant health concern that requires proactive management to prevent fractures and maintain quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management of this condition. By incorporating a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in regular exercise, and considering medical treatments when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of osteoporosis-related complications.
Ultimately, maintaining bone health is a lifelong commitment that involves a combination of lifestyle choices, medical interventions, and regular monitoring. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take control of their bone health and enjoy a life free from the limitations imposed by osteoporosis.


Leave a Reply